Challenges Facing Rural Health Care in the U.S.
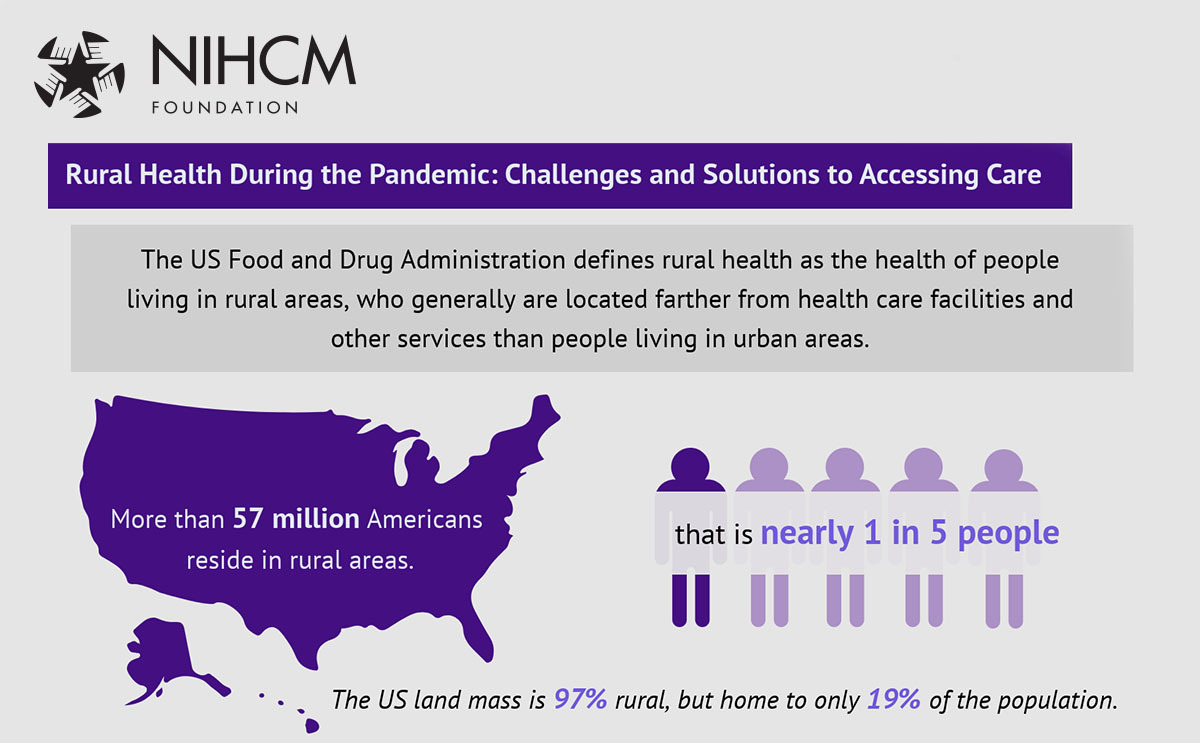
Health care in rural America faces unique challenges that differ significantly from urban and suburban areas. Although about 1 in 5 Americans live in rural communities, access to health care remains a persistent issue.
1. Limited Access to Medical Services
Rural areas often have fewer hospitals, clinics, and health care providers. Many communities may not have specialists or even a full-time physician. As a result, patients often have to travel long distances for basic care, emergency services, or specialized treatment.
2. Health Care Workforce Shortages
There is a nationwide shortage of doctors, but rural regions are particularly affected. Recruiting and retaining qualified professionals in rural areas is difficult due to limited resources, isolation, and fewer opportunities for professional development.
3. Hospital Closures
Many rural hospitals are facing financial hardship, and over 180 have closed since 2005. These closures force residents to rely on distant facilities, creating delays in care and increasing the risk of negative health outcomes.
4. Higher Rates of Chronic Diseases
Rural populations tend to have higher rates of chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and obesity. These are often worsened by limited access to preventive care and health education.
5. Transportation Barriers
Poor public transportation infrastructure makes it difficult for many rural residents—especially the elderly or disabled—to attend medical appointments.
6. Economic and Insurance Challenges
Rural Americans are more likely to live in poverty and be uninsured or underinsured. Even with Medicaid expansion in some states, affordability remains a barrier to consistent health care.
7. Mental Health Crisis
Mental health services are scarce in rural areas, and stigma around mental illness often prevents individuals from seeking help. Suicide rates are significantly higher in rural areas compared to urban ones
Moving Forward
To address these challenges, policymakers and health organizations are promoting telehealth, increasing funding for rural facilities, and creating incentives to attract health professionals to underserved areas. Strengthening rural health care is essential for the overall well-being of millions of Americans.